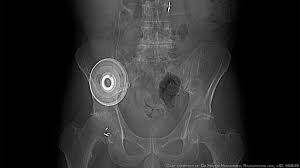
CHEMOEMBOLIZATION
Chemoembolization is a treatment for cancer that involves delivering chemotherapy directly to the tumor through the blood vessels that supply it. This is typically done through a procedure called transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), in which a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and guided to the blood vessels that supply the tumor. The chemotherapy is then delivered through the catheter, and a substance called an embolic agent is used to block the blood vessels and keep the chemotherapy in place. This helps to limit the side effects of chemotherapy, as it is delivered directly to the tumor and is not distributed throughout the body. Chemoembolization is often used to treat liver cancer, but it can also be used to treat other types of cancer.
What Is Chemoembolization:
Chemoembolization is a treatment for cancer that involves delivering chemotherapy directly to the tumor through the blood vessels that supply it. This is typically done through a procedure called transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), in which a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and guided to the blood vessels that supply the tumor. The chemotherapy is then delivered through the catheter, and a substance called an embolic agent is used to block the blood vessels and keep the chemotherapy in place. This helps to limit the side effects of chemotherapy, as it is delivered directly to the tumor and is not distributed throughout the body. Chemoembolization is often used to treat liver cancer, but it can also be used to treat other types of cancer.
What We Should Know About The Chemoembolization:
There are a few things that you should know about chemoembolization:
- It is a procedure that is done in a hospital or an outpatient center. You will be given a sedative or anesthetic to help you relax during the procedure.
- The procedure can take several hours, depending on the size and location of the tumor.
- You may experience side effects from the chemotherapy and the embolic agent. These may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue.
- The procedure may not be suitable for everyone. Your doctor will consider factors such as the size and location of the tumor, your overall health, and your treatment goals when deciding if chemoembolization is appropriate for you.
- Chemoembolization may not be a permanent cure for cancer. It is often used in combination with other treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
- You will need to follow-up with your doctor after the procedure to monitor your progress and discuss any further treatment recommendations.
Chemoembolization How To Get It?
To get chemoembolization, you will need to see a doctor who specializes in treating cancer, such as a medical oncologist or a hematologist. They will evaluate your condition and determine if chemoembolization is appropriate for you based on factors such as the size and location of the tumor, your overall health, and your treatment goals.
If chemoembolization is recommended, you will need to undergo a series of tests to prepare for the procedure. These may include blood tests, imaging tests (such as CT or MRI), and possibly a biopsy of the tumor.
Once you are ready for the procedure, your doctor will schedule it at a hospital or outpatient center. You will be given a sedative or anesthetic to help you relax during the procedure, which can take several hours depending on the size and location of the tumor.
After the procedure, you will need to follow-up with your doctor to monitor your progress and discuss any further treatment recommendations.
Chemoembolization How Its Works:
Chemoembolization is a treatment for cancer that involves delivering chemotherapy directly to the tumor through the blood vessels that supply it. This is typically done through a procedure called transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), in which a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and guided to the blood vessels that supply the tumor.
Here’s how the procedure works:
- The area where the catheter will be inserted is numbed with a local anesthetic.
- The catheter is inserted into an artery, typically in the leg or arm, and guided through the blood vessels to the tumor.
- Once the catheter is in place, chemotherapy drugs are delivered through it directly to the tumor.
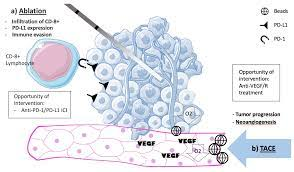
- An embolic agent, such as beads or a gel foam, is then delivered through the catheter to block the blood vessels and keep the chemotherapy in place.
- The catheter is then removed, and the puncture site is covered with a bandage.
The goal of chemoembolization is to kill cancer cells while limiting the side effects of chemotherapy by delivering the drugs directly to the tumor. The procedure may need to be repeated a few times to effectively treat the tumor.
If you want to get amazing benefits by using this link
Imaging For Low Grade Prostate Cancer
Chemoembolization Conclusion:
Chemoembolization is a treatment for cancer that involves delivering chemotherapy directly to the tumor through the blood vessels that supply it. This is typically done through a procedure called transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), in which a catheter is inserted into an artery in the leg or arm and guided to the blood vessels that supply the tumor. The chemotherapy is then delivered through the catheter, and a substance called an embolic agent is used to block the blood vessels and keep the chemotherapy in place. This helps to limit the side effects of chemotherapy, as it is delivered directly to the tumor and is not distributed throughout the body. Chemoembolization is often used to treat liver cancer, but it can also be used to treat other types of cancer.
It is important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of chemoembolization with your doctor before deciding if this treatment is right for you. They will be able to determine if you are a good candidate for the procedure and help you understand what to expect during and after the procedure.
