If you’re familiar with capacitors and resistors, then you’ll know that a diode is basically the simplest semiconductor that is able to perform a variety of functions, thus they also come in different forms. Today, we will be addressing everything you need to know about diodes.
Notwithstanding, before we can bounce solidly into our fundamental top story, how about we take a gander at the essential ideas you ought to realize that would assist you with better figuring out diodes:
Note: Briefly describe the Introduction to Diode, Pinout, Working, Features & Applications
Overview of Diodes
What is a diode?
Voltage: Distinction in electricity possible between two focuses.
Resistor: A latent two-terminal electrical part that carries out electrical opposition as a circuit component.
Capacitor: A latent part that stores electrical energy in an electric field.
Semiconductor: A semiconductor gadget that is worked with three terminals for intensifying or exchanging electronic signs and electrical power purposes.
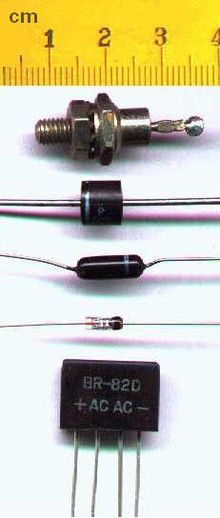
A diode is a two-terminal semiconductor gadget that permits current to just move through in one course. It fundamentally has irrelevant opposition toward one side and high obstruction on one more to keep the current from moving through the two different ways. In this way, a diode resembles a valve in an electrical circuit.
Construction of a diode
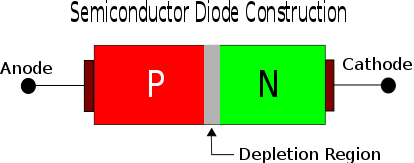
There are really many sorts of diodes, however, we will discuss the development of a fundamental semiconductor diode here.
As we referenced, a diode is a semiconductor subsequently it is made from one or the other silicon or geranium. From the picture above, you can likewise see that diode has two terminals, Anode and Cathode, P intersection and the N intersection. While the consumption area is for the electrons to move through.
How does the diode work?
How a diode work relies upon the cooperation between the P and N intersection. In an ordinary situation, P has a high convergence of openings and a low centralization of free electrons while N has a lower grouping of openings and a higher centralization of free electrons, the electrons will move towards P and permit the current to just course through P.
The above clarification just applies to what might generally occur, presently we should check out at a portion of the exceptional situations:
Forward Biased Diode
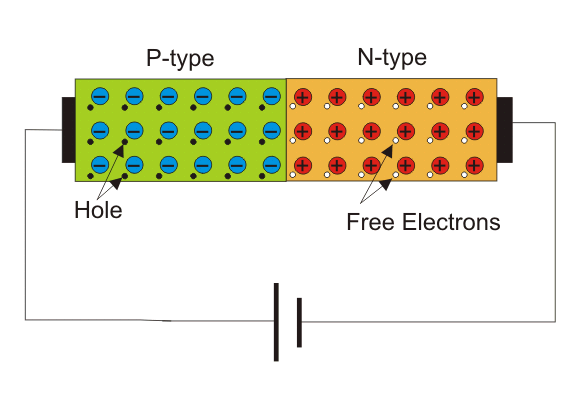
This would happen when a positive terminal of a source is associated with the P intersection and the adverse terminal of the source is associated with the N intersection of the diode while expanding the voltage gradually from nothing.
There will be no ongoing coursing through toward the start because of the possible hindrance. In any case, on the off chance that the outside voltage applied to the diode is bigger than the forward expected hindrance, the diode will go about as a shortcircuited way while the ongoing will really at that time be restricted by outer resistors.
Reverse Biased Diode
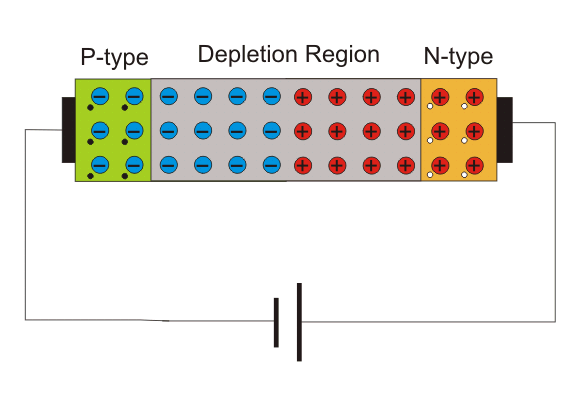
This would happen when the voltage source is associated with the adverse terminal of the P intersection and the voltage source is associated with the positive terminal of the N intersection.
As may be obvious, this has a contrary impact on the forward-one-sided diode. Because of the electrostatic fascination, the openings in the P intersection would be moved further away from the exhaustion district leaving more revealed negative particles at that area. At the point when this happens, the progression of current will then be impeded, permitting no current to course through the circuit.
Unbiased Diode
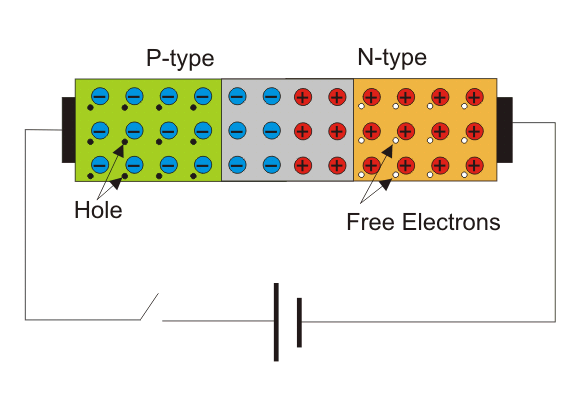
At the point when the P and N intersection interacts with one another, the openings will begin diffusing from the P intersection to the N intersection as well as the other way around. This is because of the distinction in centralization of openings as referenced before. Ultimately, the electrons will be recombined in the consumption locale, and there would be no more dissemination of charges.
Summary
Also, that is all on diodes! Did you gain some new useful knowledge about diodes now? We trust that with this information, you’ll have the option to analyze and use diodes in your future tasks!

