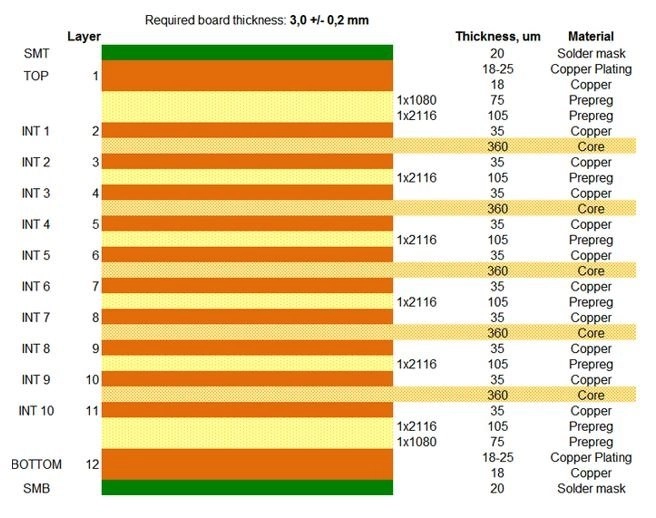
Nowadays, PCBs are used in virtually every electronic device that you know of – from your laptop to your smartphone to the most complex supercomputer. In this blog article, we look at the many different materials that make up a 12-Layer PCB stack-up and how it is assembled.
What is a PCB Stackup?
PCBs are printed circuit boards, which are a type of electronic component. They consist of layers of metal and plastic that have been laminated together. PCBs can be configured in many different ways, including stackups. A stackup is the arrangement of multiple PCBs on a single substrate.Stackups can be beneficial for a variety of reasons. For example, stackups can simplify the design process by eliminating the need to create multiple PCB layouts. Stackups can also improve the flexibility and functionality of an electronics system. Finally, stackups can reduce the cost and time required to produce an electronic product. 12 layer pcb stackup
Why is a PCB Stackup Important for PCB Manufacturers?
A PCB stackup is important for PCB manufacturers because it determines the overall height, width, and depth of a PCB. The layout of the layers in a stackup affects how easily traces can be made between layers, how well electricity can flow through the board, and how heat will dissipate. A PCB stackup also affects the weight and cost of a board.
A PCB stackup is created when an electronic design is imported into a PCB manufacturing program. The program creates a three-dimensional image of the pins, pads, and other features on the board. The layout of each layer in this image is then placed on top of one another in a specific order to create the final stackup.
The order in which layers are placed on top of each other is called the “topology” of a stackup. There are three types of topologies: flat-topology, double-sided-topology, and hybrid-topology. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Flat-topology stacks up all layers in a single plane with no curves or angles. This type is easy to layout because there are no obstructions along trace routes between layers. However, flat-topology boards are heavy and expensive due to their greater thicknesses compared to other topologies. Double-sided-topology sandwiches two sheets of paper together so that both sides have the same layout information (pins, pads, et cetera).
What is the Market Size for 12 Layer PCB Stackups?
According to a recent report, the global market for 12 layer pcb stackups is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.5% during the forecast period 2018-2025. The market has been witnessing a rise in demand from various industries owing to the increasing requirement for more efficient and reliable circuits.
The key factors driving the growth of the 12 layer PCB stackup market include:
1) Increase in use of 12 layer PCBs in high-end devices
2) Increasing demand from automotive and electronics sectors
3) Increasing demand from aerospace and defense industry
What are the Different Types of 12 Layer PCB Stackups?
There are a variety of different types of 12 layer PCB stackups. These include single-sided stackups, double-sided stackups, and even stacked up 12 layers high! The most common type of 12 layer PCB stackup is the double-sided stackup. This involves stacking two pieces of PCB together so that they form a single piece with two surfaces. Other types of 12 layer PCB stackups include single-sided stackups and stacked up 12 layers high!
The advantage to using a 12 layer PCB stackup is that it can increase the overall strength and stability of the board. Additionally, it can reduce the amount of space required for the board, which can be helpful when space is limited. While a 12 layer PCB stackup may require more time and effort to create than some other types of stacks, it can be very rewarding in terms of the final product.
Conclusion
If you are working with 12-layer PCB stackups, it is important to understand the risks and benefits of doing so. By understanding the risks and benefits, you can make an informed decision about whether or not to use a 12-layer PCB stackup in your next design project.